What are the treatment options for Carotid Artery Stenosis?
The treatment options for carotid artery stenosis will depend upon the primary detection of the condition prior to a Transient Ischaemic Attack (TIA) or a Stroke. Therefore, the treatment may be separated into medical or interventional treatment options.
Additionally, the severity of the obstruction or plaque build-up within the carotid artery will determine which treatment options are most appropriate for each individual patient.
Medical treatment
Medical treatment for carotid artery stenosis can be divided into lifestyle and medications.
Lifestyle changes can include:
- Cessation of smoking,
- Weight loss,
- Maintaining a healthy low-fat diet, and
- Regular exercise.
Medications may be administered to control the presence of:
- Hypertension and
- Cholesterol levels.
Interventional Treatment
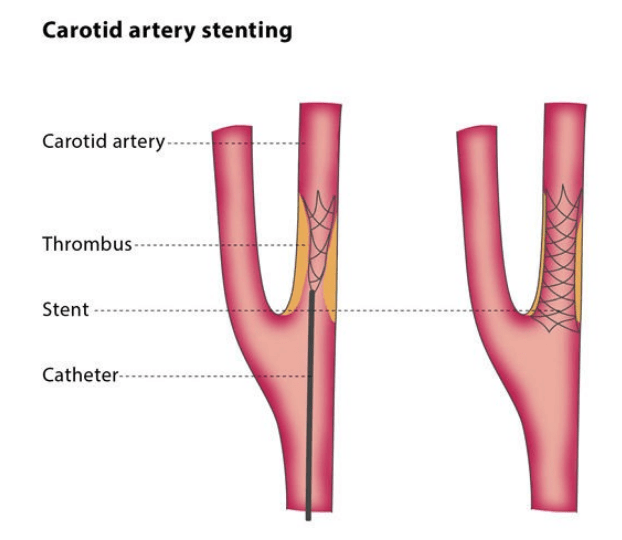
Interventional treatment may be a consideration depending on the level of obstruction within the carotid artery. These procedures can include, carotid angioplasty and stenting.
Similar to coronary angiography, in carotid artery stenting, a small catheter is introduced into the carotid artery and a balloon is inflated to widen the narrowed artery. Following this, a small mesh wire stent is left within the obstruction to ensure that the artery remains open, to ensure increased blood flow to the brain through the damaged carotid artery.
Understanding Carotid Stenting and Endarterectomy procedures
