About Bradycardia
Bradycardia is an arrhythmia characterised by a slow heart rate, usually 60 beats per minute. When the heart rate is too low, the heart may be unable to meet the metabolic needs, such as cardiac output or blood pressure of a person, and cause them to feel faint, dizzy, or collapse. In some people, slow heart rates may be normal during periods of rest, sleep, or if a person is very physically fit, but generally, slow heart rates may limit activity and patients may exhibit symptoms.1
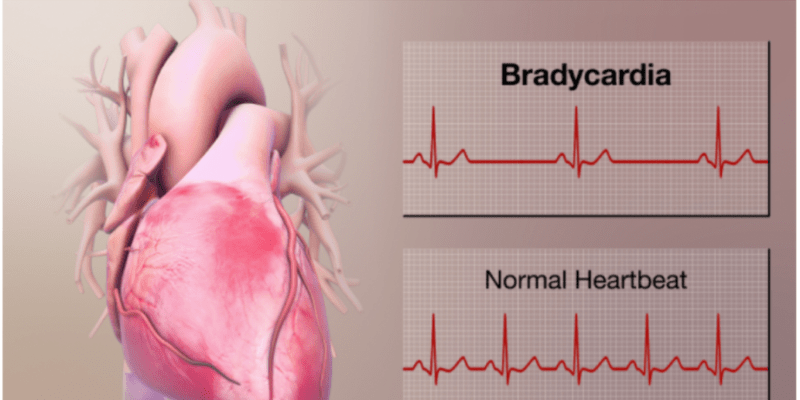
Causes of Bradycardia
There are many causes for bradycardia. A common cause can be due to abnormalities in the electrical pathway from the sinoatrial (SA) node to the ventricles, impacting the heart’s ability to receive the stimulation from the SA node and adequately “beat.” Under normal circumstances, this impulse starts in the SA node, conducts through the septum via the AV node, and continues to the ventricles. If there is a disruption to the normal electrical conduction, the heart rate may be slowed or in some cases become non-existent.
Additionally, some patients may be diagnosed with a condition called ‘heart block’, whereby the electrical stimulus from the SA node is not conducted to the ventricles or is “blocked” due to conduction issues with the AV node and in turn leading to slow heart rates.
Below is an illustration of normal cardiac electrical conduction.
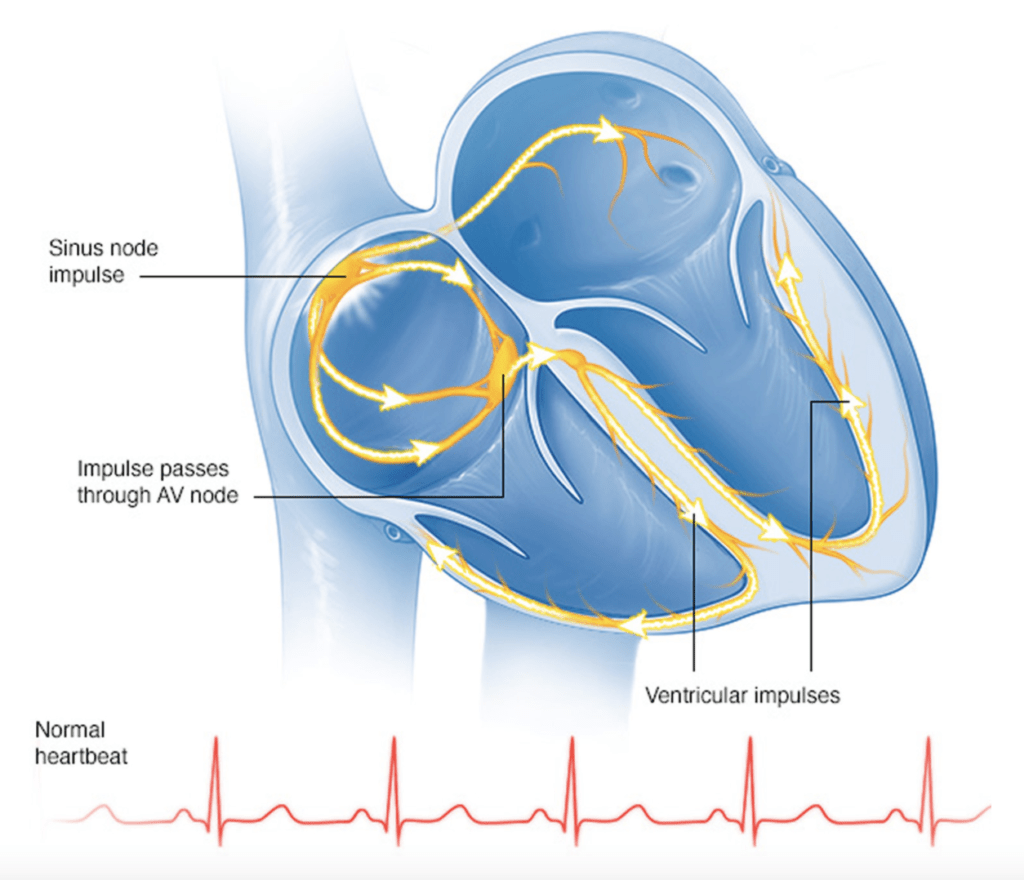
These classifications are:
- First-degree heart block – when there may be a delay in the electrical signal passing from the SA node to the ventricles
- Second-degree heart block – when some though not all electrical signals from the SA node are conducted to the ventricles, allowing the heart to “drop” a beat from time to time and become irregular
- Third-degree heart block – often referred to as “complete heart block” when most (if not all) electrical signals from the SA node are “blocked” from the ventricles which results in a very slow heart rate.2
Other causes of bradycardia may be:
- Ageing may slow the condition system of the heart
- Heart attacks may damage the electrical stimulation pathways
- Congenital heart defects
- Myocarditis (heart infections or inflammatory disorders such as Lupus)
- Heart valve surgery
- Cardiac trauma
- Hormonal imbalances such as hypothyroidism
- Electrolyte disturbances such as low potassium levels
- Sleep apnoea
- Many medications can cause slow heart rates
